Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Core Benefits of Decentralized Domains
- How Decentralized Domains Work
- Key Applications in Web3 Ecosystem
- Setting Up and Using Decentralized Domains
- Future Trends and Challenges
- Conclusion
Introduction
What Are Decentralized Domains?
In the evolving landscape of the internet, decentralized domains represent a transformative shift from traditional domain name systems (DNS) to blockchain-based domain management. Unlike conventional domains managed by centralized authorities such as ICANN, decentralized domains operate on distributed ledger technology, predominantly using blockchain networks. This shift empowers users with complete ownership and control over their domains without relying on intermediaries, drastically reducing vulnerabilities such as censorship, hijacking, or unilateral takedown.
Decentralized domains are registered and managed on blockchain protocols, making all ownership records immutable and transparent. For example, instead of a domain like "example.com," users can register domains ending with extensions like .eth or .crypto. This blockchain-backed domain name acts as a public key alias that simplifies cryptocurrency wallet addresses and links directly to decentralized identities and services.
Why They Matter in Web3
The rise of the Web3 movement emphasizes decentralized control, user autonomy, and censorship-resistant applications, positioning decentralized domains as critical infrastructure. They enable what experts call digital sovereignty by allowing individuals and organizations to manage their online identity autonomously, without intermediaries that could impose restrictions or control over content.
Decentralized domains also enhance security and resilience in cyberspace by distributing domain management across a blockchain network rather than central servers. This model prevents single points of failure and reduces the risk of domain theft or malicious interference. Moreover, the inherent censorship resistance empowers users facing oppressive regimes or restrictive platforms to maintain a free and accessible web presence.
For businesses and developers, decentralized domains offer seamless integration with decentralized applications (dApps), enabling innovative marketing, identity, and social tools that mesh naturally with blockchain wallets and digital assets. Platforms like Hashtag.it.com leverage these advantages to provide comprehensive solutions for Web3 domain management, promoting autonomy and monetization of digital identities.
Note: Decentralized domains are rapidly becoming foundational to online freedom and identity in the emerging decentralized internet.
Core Benefits of Decentralized Domains
Enhanced Security and Ownership
Blockchain-based decentralized domains provide immutable ownership records and enhance security by eliminating reliance on centralized registrars vulnerable to hacks or seizure. Once a domain is registered on a blockchain like Ethereum via the Ethereum Name Service (ENS), ownership is permanently recorded and controlled solely by the user’s wallet key. This decentralized authentication prevents domain hijacking and phishing attacks common with traditional domain systems.
Additionally, users benefit from full sovereignty over their domain — they can transfer, sell, or utilize it without restrictions imposed by intermediaries. The transparent blockchain ledger enables easy verification of domain authenticity, reducing fraud risks highlighted in blockchain domain fraud prevention research.
Moreover, the integration of smart contracts automates renewals and transfers, minimizing administrative overhead and human error. This security architecture fortifies domain management beyond what traditional DNS systems offer.
Censorship Resistance
One of the most profound advantages of decentralized domains is their ability to resist censorship. Traditional domains controlled by centralized entities can be seized, suspended, or blocked by governments or corporations. In contrast, decentralized domains are stored on blockchain networks that operate without centralized control, making takedown or censorship attempts ineffective.
Decentralized domains enable permanent content availability, allowing activists, journalists, and content creators to host sensitive or controversial materials safely. This capability is vital in oppressive political climates where freedom of speech is curtailed. Projects like censorship-resistant publishing illustrate how decentralized domains facilitate an uncensorable web presence.
Key Insight: Decentralized domains empower digital freedom by safeguarding online content from interference and promoting a free flow of information.
Improved Digital Identity
Decentralized domains significantly advance digital identity management by acting as verifiable, user-owned identifiers that link to blockchain wallets and decentralized credentials. Users gain privacy, control over their personal data, and ability to present verifiable credentials across multiple platforms (see digital identity management).
They support the concept of self-sovereign identity, enabling users to authenticate to dApps and Web3 services without surrendering control to central authorities, thereby reducing risks of identity theft and improving trustworthiness online.
These domains foster interoperability across blockchain ecosystems, simplifying interactions with finance, social media, and other decentralized applications. This integration enhances user experience while reinforcing security and autonomy.
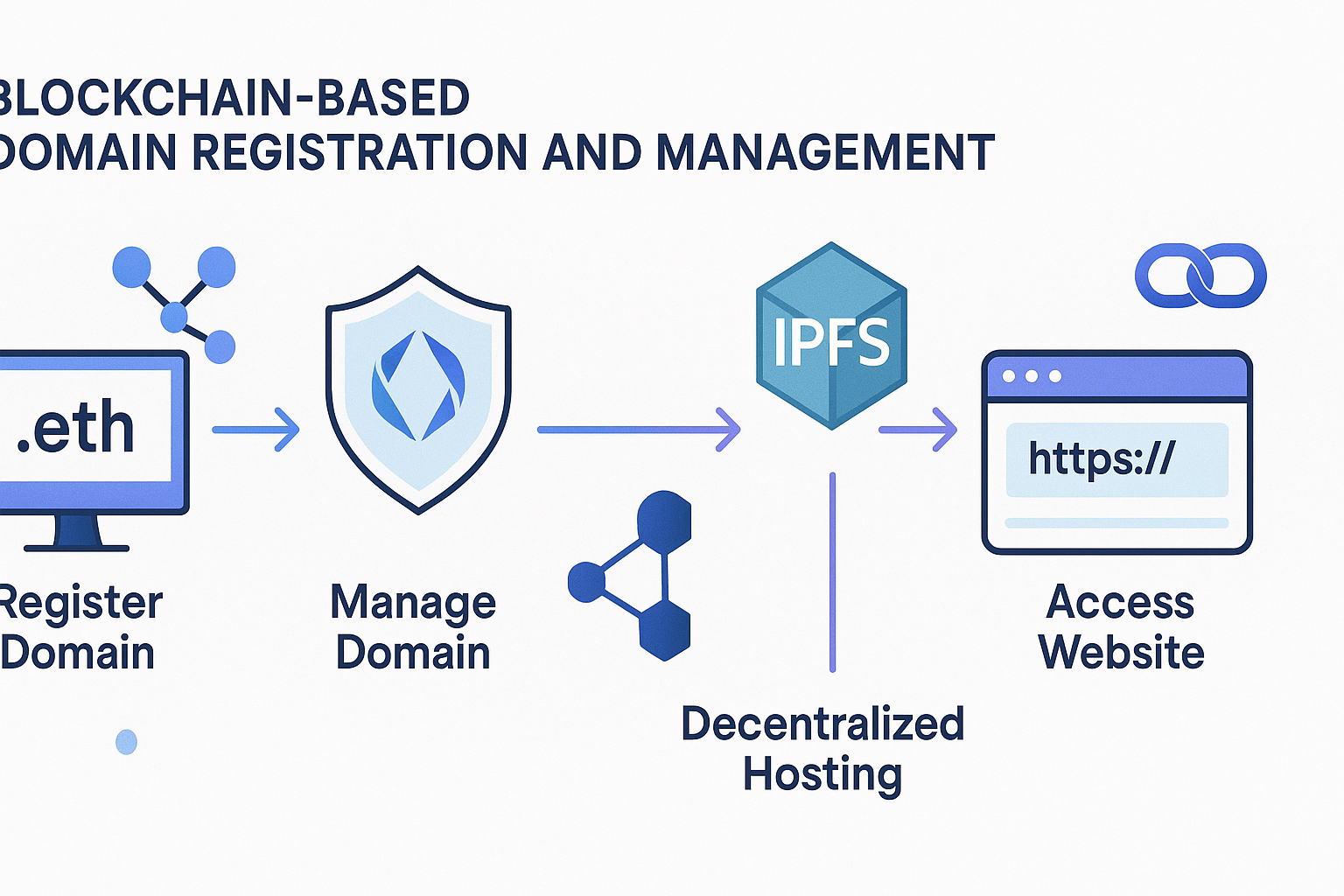
How Decentralized Domains Work
Blockchain Technology and Protocols
Decentralized domains use robust blockchain networks such as Ethereum, Handshake (HNS), and innovative protocols like 3DNS to record domain ownership and manage domain name resolution. These blockchains ensure that domain data is immutable, transparent, and distributed across numerous nodes, eliminating central points of failure.
The ENS protocol is among the most prominent systems, leveraging Ethereum smart contracts to register .eth domains. Handshake provides a permissionless alternative focused on decentralization with its own TLD auction system. 3DNS combines blockchain with traditional DNS to enable instantly liquid, NFT-based domains, creating a hybrid ecosystem.
These protocols support robust security features, including cryptographic signatures and smart contract automation, underpinning trustless domain management.
Domain Registration and Management
Registering a decentralized domain typically involves connecting a cryptocurrency wallet and selecting a domain through platforms like ENS or Unstoppable Domains. The payment is made in cryptocurrency, and the transaction is recorded on the blockchain, granting immediate, verifiable ownership.
Management involves interacting with smart contracts to update records such as IPFS hashes or subdomains, transfer ownership, or adjust permissions — all transparently recorded and immutable. This process is decentralized, preventing unilateral changes by any third party.
The process enhances security, transparency, and user control, facilitating new possibilities for domain-related applications such as identity verification and decentralized hosting.
Integration with Decentralized Hosting
Decentralized domains operate seamlessly with hosting solutions like the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), enabling the deployment of censorship-resistant websites. IPFS stores content in a distributed network rather than single servers, ensuring higher resilience and permanence.
When a decentralized domain points to an IPFS hash, users accessing the domain retrieve content directly from the decentralized network, avoiding centralized servers vulnerable to shutdowns or censorship.
This integration makes it possible to host uncensorable websites, critical for free speech advocates, journalists, and content platforms requiring guaranteed uptime and content integrity.
Key Applications in Web3 Ecosystem
Censorship-Resistant Publishing
Decentralized domains empower publishers and activists to bypass traditional content restrictions. By hosting content on decentralized platforms using blockchain domains, creators avoid arbitrary takedowns and content limitations commonly enforced by centralized platforms.
Case studies reveal that journalists operating under authoritarian regimes use decentralized domains to maintain blogs and news sites that remain accessible despite governmental internet shutdowns. Activists utilize these platforms to spread awareness and organize without fear of domain seizure, enhancing online safety and freedom.
This application supports the broader vision of a free, open internet where diverse voices cannot be silenced.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Identity
In the evolving DeFi space, decentralized domains provide a secure and verifiable identity layer that integrates directly with blockchain wallets and smart contracts. Users register domains like alice.eth, linking them to their DeFi profiles, enabling seamless authentication and reducing fraud.
This identity verification mechanism helps platforms comply with KYC/AML regulations without compromising user privacy. Moreover, it supports permissioned access to financial services such as lending platforms, decentralized exchanges, and governance voting.
The rise of DeFi amplifies the value of blockchain domains as essential tools for trustless identity management.
Digital Identity and Authentication
Decentralized domains also serve as pillars of digital identity and authentication in Web3 environments. They enable self-sovereign identity frameworks where users control credentials issued across multiple platforms, verified cryptographically and privacy-preservingly.
This approach mitigates risks of centralized data breaches and enhances interoperability across decentralized applications. Users authenticate seamlessly without passwords, improving security and user experience.
Decentralized identity solutions linked to domains simplify onboarding for dApps, promoting broader adoption of decentralized services.
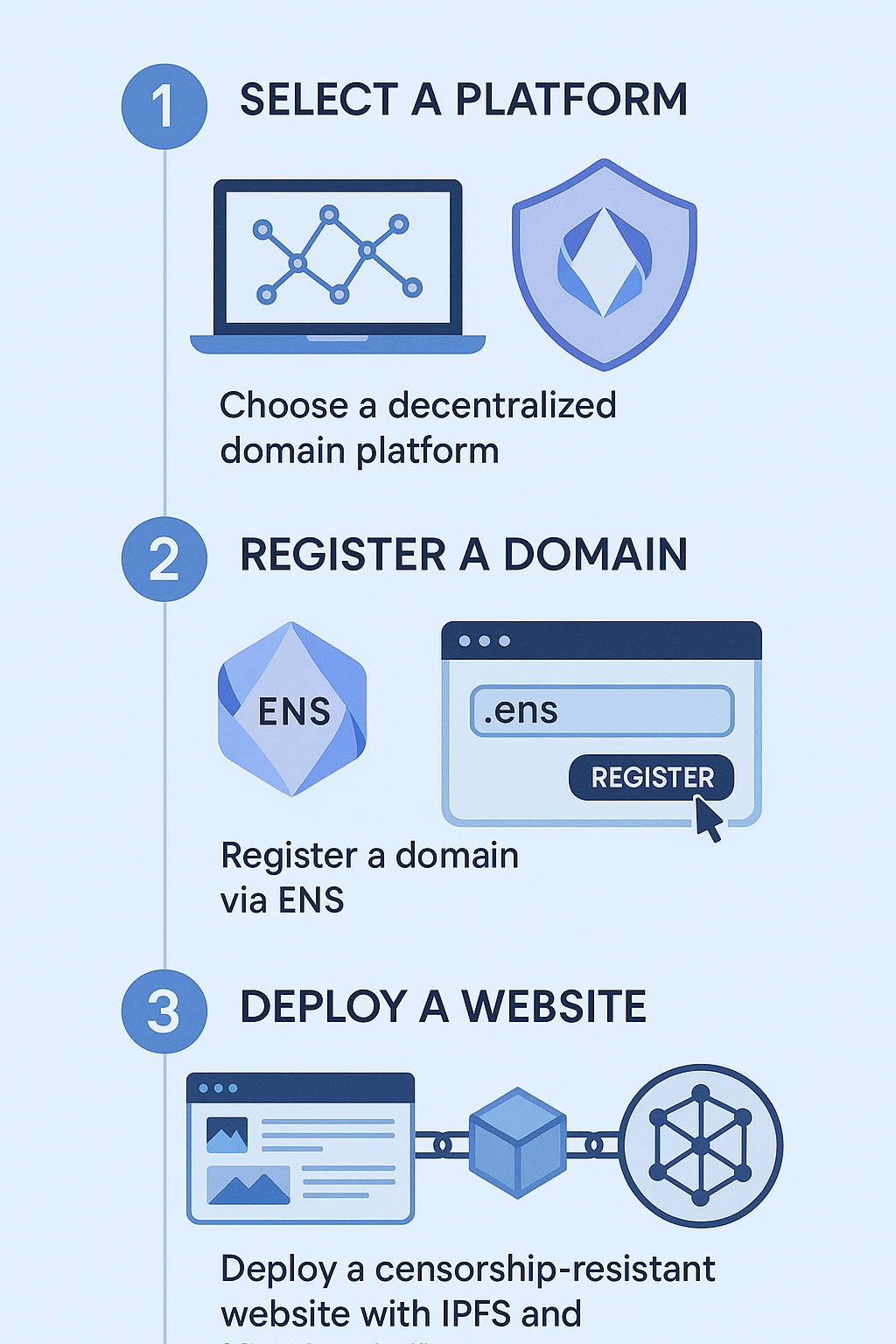
Setting Up and Using Decentralized Domains
Choosing the Right Platform
Selecting a decentralized domain platform depends on specific needs such as desired TLDs, compatibility, and ecosystem support. Popular options include:
- Ethereum Name Service (ENS): Ideal for Ethereum-based applications with
.ethdomains, supported by broad dApp integration and strong community backing. - Handshake (HNS): Suitable for users seeking a fully decentralized TLD auction mechanism and censorship resistance.
- 3DNS: Hybrid model that combines traditional DNS with blockchain features for liquidity and NFT-based ownership.
- Unstoppable Domains: Offers domains like
.cryptoand.zil, emphasizing user-friendly interfaces and integration with decentralized hosting.
Evaluating platform features helps users align domain choices with intended Web3 use cases.
Registering and Configuring Domains
Registration involves connecting a compatible wallet, selecting the domain, and completing payment in cryptocurrency. After acquisition, users configure domain records—linking to decentralized storage (e.g., IPFS hashes), setting up subdomains, and choosing resolvers.
Follow platform-specific guides such as Ethereum Name Service (ENS) documentation to ensure proper configuration for accessibility and security.
Verification of setup can be done by resolving the domain in Web3-enabled browsers or gateways.
Building Censorship-Resistant Websites
Deploying a censorship-resistant website requires:
- Uploading site content to IPFS or another decentralized storage.
- Pinning content via services to ensure availability.
- Linking the decentralized domain to the content hash.
- Ensuring ongoing maintenance and monitoring.
This process guarantees permanent availability and protection against domain takedown and content censorship, creating a resilient online presence.
Future Trends and Challenges
Market Growth and Adoption
The decentralized domain market is projected to grow significantly as digital sovereignty and Web3 adoption accelerate. User demographics are expanding beyond crypto enthusiasts to include content creators, marketers, and enterprises exploring blockchain for secure digital identity.
Industry trends indicate rising demand for user-controlled digital assets and the integration of decentralized domains into mainstream applications, fueling market expansion and innovation.
Technological Innovations
Advancements include NFT-based domain minting for instant liquidity, smart contract automation for renewals and transfers, and improved interoperability across blockchain networks. Additionally, AI integration enhances domain suggestions and cybersecurity, while zero-knowledge proofs provide privacy-preserving management.
Hybrid models combining traditional DNS features with blockchain benefits also evolve, expanding usability.
Regulatory and Governance Issues
As decentralized domains challenge traditional internet governance, regulatory bodies are grappling with applying jurisdiction, intellectual property laws, and dispute resolution in a borderless environment.
Innovative on-chain arbitration and decentralized governance models are emerging to address misuse, trademark disputes, and legal accountability. However, regulatory clarity and international cooperation are vital to balancing innovation with security.
Conclusion
Decentralized domains represent a revolutionary advancement in digital identity, security, and freedom on the internet. Through blockchain technology, they provide enhanced user ownership, censorship resistance, and interoperability, critical for the unfolding Web3 ecosystem.
Key Takeaways:
- Empowered ownership ensures users have total control over their digital identity and domain assets.
Censorship resistanceprotects freedom of expression by preventing centralized takedowns and domain seizures.- Improved digital identity systems foster trust, privacy, and seamless interaction across decentralized applications.
Embracing decentralized domains is a strategic step toward securing your digital future and harnessing the full potential of the decentralized web.
Explore decentralized domains today to secure your digital identity and embrace the future of the internet.
References
- An Analysis of 3DNS, ENS, HNS, and GoDaddy
- Create a Decentralized Website | support.ens.domains
- Beginner’s Decentralized Identity Guide for 2025
- Philosophical Perspectives on Decentralized Identity
- ICANN vs. Web3 Registrars
- The Expanding Ecosystem of Web3 TLDs: From .eth to .dao, What’s Next?
- Decentralized Credential Status Management: A Paradigm Shift in Digital Trust
- Trustless Autonomy: Understanding Motivations, Benefits and Governance Dilemma in Self-Sovereign Decentralized AI Agents
- What is a Web3 TLD?
- Decentralized Domain Platforms Utility
Leave a Reply