Table of Contents
- Why Web3 Identity Matters
- Core Identity Fundamentals
- Security And Privacy Foundations
- Standards And Protocols
- Platform And Vendor Survey
- Real-World Use Cases
- Developer Implementation Guide
- Governance Recovery And Control
- Future Trends And Outlook
- Common Questions Answered
- Next Steps For Adoption
Why Web3 Identity Matters
Digital identity has entered a transformative era where ownership, privacy, and portability are now possible through decentralization. Web3 digital identity management offers users the tools to control their identity on their terms — a radical shift away from the gatekeeping of legacy providers. By combining decentralized identifiers (DIDs), verifiable credentials (VCs), and self-sovereign identity (SSI) principles, the next-generation internet enables secure logins, credential exchanges, and data portability for users everywhere. Whether you are a developer, business leader, or privacy advocate, understanding these principles is essential for navigating this new digital landscape.
Target Audience And Scope
This guide serves a diverse audience — from engineers and product managers to marketers and privacy-focused individuals. You will learn the building blocks of Web3 identity, how blockchain secures these new forms of identification, and why moving your digital credentials to decentralized models is both safer and more empowering. For growth hackers and affiliate marketers, the rise of the web3 affiliate marketing platform changes how tracking, attribution, and rewards work, making trustless, transparent, and privacy-centric programs possible.
Key Concepts At A Glance
- Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs): New cryptographically-secure IDs you control, not issued by a corporation.
- Verifiable Credentials (VCs): Digitally signed claims about you (e.g., academic degrees or membership cards) that can be checked without revealing everything about you.
- Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI): A governance model where users own and manage their identity and data autonomously.
- Web3 domains: Unique, censorship-resistant domains (NFT Domains Explained) that double as user IDs and support wallet logins, credential issuances, and more.
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs): Advanced cryptography allowing you to prove facts about yourself without exposing private data (Zero-Knowledge Proofs Feature).
The technical underpinnings — blockchain anchoring, immutability, cryptographic keys, and ZKPs — establish unforgeable audit trails and privacy-centric authentication. These foundations are transforming identity use cases in healthcare, finance, and the supply chain, elevating user autonomy and trust across the web.
Core Identity Fundamentals
Web3 digital identity management is a framework in which individuals and organizations create, control, and use their own digital identities without reliance on centralized authorities. This move democratizes access, enhances privacy, and supports seamless credential verification across ecosystems.
Decentralized Identifiers Explained
W3C DID Core standardizes DIDs, providing universally unique, cryptographically secured identifiers across blockchains and web protocols. Leading methods include:
- did:key: Simple, locally generated IDs using public key cryptography.
- did:web: Leverages DNS and HTTPS for domain-hosted DIDs, bridging web2/web3.
- did:ethr: Ethereum/EVM-based DIDs anchored to smart contracts and on-chain keys.
Resolvers interpret these to produce the public keys and service endpoints needed for verification. Each DID method varies by storage, security, and onboarding patterns, shaping how identities are created and trusted (Ethereum Decentralized Identity).
Verifiable Credentials And Claims
Verifiable Credentials (VCs) are digital attestations (claims) securely issued by trusted parties. Each VC contains cryptographic proofs, allowing recipients to confirm authenticity without involving the issuer. The core roles:
- Issuer: Creates and signs the VC.
- Holder: Stores the VC in a wallet.
- Verifier: Inspects and validates the VC presented by the holder.
This model supports privacy, selective disclosure, and revocation. Credentials can represent anything from professional certifications to medical records, with Dock Web3 Identity leading implementations in wallets and dApps.
Self-Sovereign Identity Principles
SSI lets users independently manage credentials, decide what to share, and grant or withdraw consent at any time. By prioritizing portability, consent, and minimal disclosure, users experience greater agency and privacy. Regulatory compliance and cross-border interoperability are further facilitated by open standards.
Web3 Domains As Identity
Web3 Domain Services and names like ENS, NFT domains, and hashtag domains turn the very address of your online activity into a persistent, user-owned identifier. Owning a Web3 Domain Platform means your wallet, website, and even your social media persona can be integrated, discoverable, and secure. These serve as both your digital brand and verification endpoint, mapping easily onto Web3 Domain Services and supporting logins, payments, and social reputation across ecosystems.
Centralized Vs Decentralized Models
Legacy authentication protocols (OAuth, SAML) rely on brokers like Google or Facebook to grant access. In contrast, DIDs and VCs decouple authentication from any provider, eliminating single points of failure and surveillance. Selective disclosure and cryptographic proofs ensure users remain in full control, greatly improving privacy and resistance to account lockout or manipulation. For organizations, this results in enhanced compliance, user trust, and ecosystem interoperability (Endless Domains Ownership).
DID Standards Comparison
| Standard | Primary Use | Interoperability | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| DID Core (W3C) | Universal data model | High | Canonical for all method implementers |
| did:ethr | EVM stack & dApps | Medium (EVM-centric) | Great for Ethereum/NFT/blockchain projects |
| did:key | Peer/local/ephemeral | High | Lightweight, easy for quick onboarding |
| did:web | Hosted on websites | Medium (web-native) | Bridges web2-web3, no blockchain required |
In the modern digital landscape, decentralized identity isn’t just a privacy upgrade—it’s a paradigm shift toward genuine user agency and internet-wide portability.
Security And Privacy Foundations
Security and privacy form the backbone of web3 digital identity management, leveraging blockchain and cryptography to deliver tamper resistance, auditability, and selective exposure of sensitive data.
Blockchain Anchoring Benefits
Anchoring proofs or metadata on-chain ensures any credential or claim can be audited—impossible to fabricate or alter after issuance. This immutability supports data integrity and tamper-evidence, but also presents challenges for data redaction (e.g., “right to be forgotten”). Systems balance this by anchoring only hashes while keeping private data off-chain.
Cryptography And Key Management
Robust management of public/private keys guards against fraud, hacks, and impersonation. Hardware wallets and multi-factor authentication increase protection, while key rotation and revocation mitigate compromised keys. Custody models (self, managed, hybrid) offer flexibility but shift responsibility for loss and recovery.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs In Identity
Zero-Knowledge Proofs Feature empower privacy-preserving verification: parties can prove eligibility or attribute possession (e.g. age, citizenship) without disclosing specifics. As noted by Dock, ZKPs become vital for “passwordless” authentication, selective disclosure, and consent-based access — all without leaking underlying personal information.
Threat Models And Mitigations
Systems must anticipate replay attacks, key compromise, Sybil attacks (fake identities), and social engineering. Countermeasures include on-chain revocation registries, biometric or social recovery, and hybrid off-chain storage to minimize exposure. Rigorous security audits, bug bounties, and continuous monitoring further improve defense.
Privacy And Compliance Considerations
Immutability collides with the need to redact or obscure user data for compliance (GDPR, HIPAA). Best practices use off-chain storage and encrypted pointers, with privacy-by-design approaches that minimize data collection from the outset. Domain ownership and Web3 profiles must be carefully managed to avoid unintended traceability or surveillance (ArXiv Decentralized Identity Paper).
Privacy Techniques Comparison
| Technique | What It Protects | Trade-Offs | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| On-Chain Hashing | Data integrity, audit | Linkability if misused | Timestamps, credential anchors |
| Off-Chain Storage | Confidential data | Trust, availability risks | Medical/financial records |
| Zero-Knowledge Proofs | Private attribute proof | More compute, steeper learning | Age checks, KYC, limited disclosure |
| Revocation Registries | Prevent misuse | Added complexity, availability | Employment, supply chain, licensing |
Standards And Protocols
Web3 identity standards ensure interoperability and future-proofing. The W3C DID Core and Ethereum Decentralized Identity frameworks set the baseline for secure identifiers and credential exchange.
W3C Standards Overview
DID Core and VC Data Model define the structure, lifecycle, and cryptographic semantics for decentralized IDs and claims. Compliance with these is vital for ecosystem-wide authentication and trust.
Interoperability Layers
Resolvers (for DIDs), registries, and bridges like the Cross-Chain Asset Interoperability Protocol (CAIP) allow seamless use of identifiers and proofs across blockchains. DIDComm and OIDC4VP protocols further enable secure exchange and presentation of credentials. Tools like Microsoft Decentralized Identity bring enterprise integrations to the cloud.
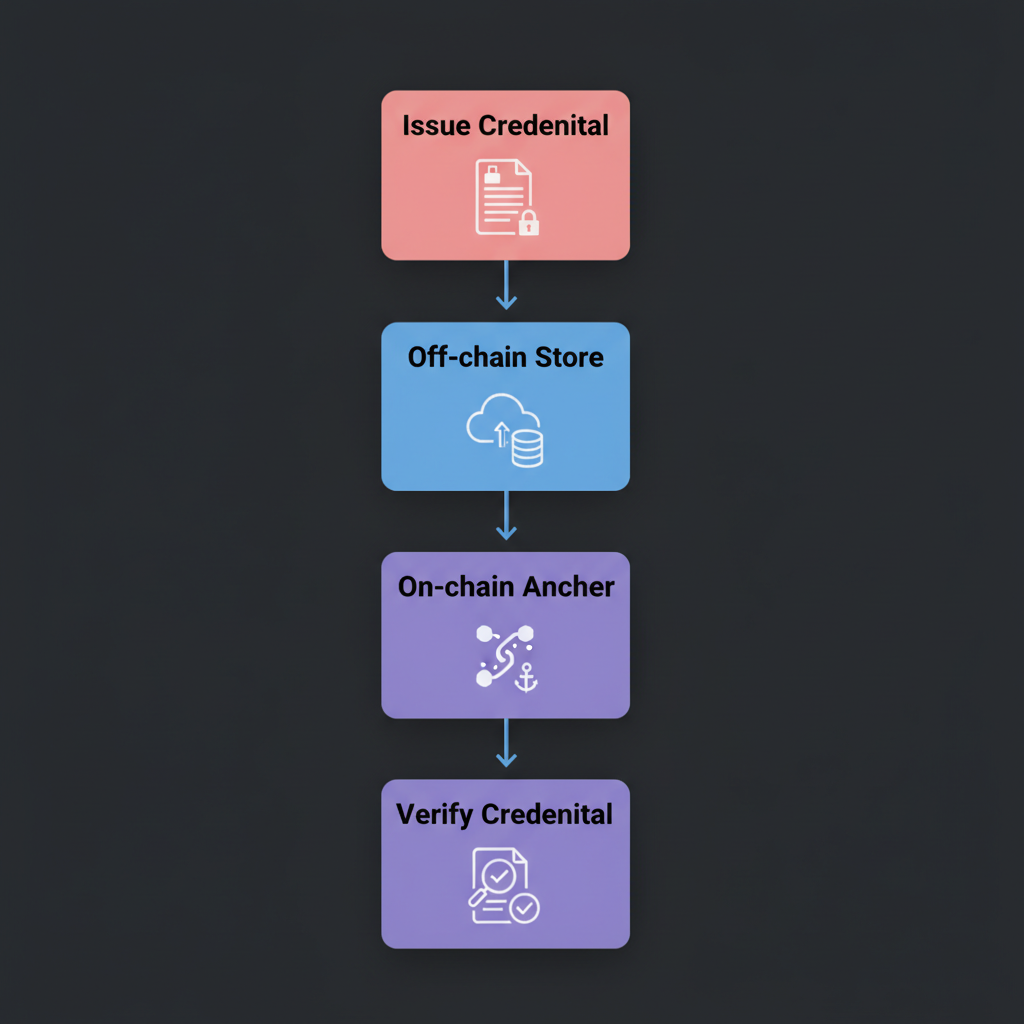
Verification Flows
Standardized flows follow: issuance (of credentials by an issuer), storage (with the user), and presentation (to a verifier). Presentations are designed to minimize data leakage while maximizing proof.
Middleware And SDKs
Popular SDKs and middleware help developers integrate DIDs/VCs into apps, manage wallet flows, and conduct revocation checks. These tools abstract much of the cryptographic complexity and expose REST APIs or JavaScript libraries for rapid prototyping.
Protocol Stack Comparison
| Layer | Common Protocols | Strengths | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identifier | DID Core, did:ethr | Decentralized, flexible | Method adapters required |
| Credential | VC Data Model | Secure, portable claims | Varies in standard maturity |
| Presentation | OIDC4VP, DIDComm | User consent flows, privacy | Cross-wallet UX variation |
| Interoperability | CAIP, custom bridges | Cross-chain reach | Trust and engineering overhead |
Platform And Vendor Survey
The web3 identity ecosystem is rich and evolving, supporting both corporate and open-source needs across the global market.
Enterprise Solutions
Leaders like Microsoft Decentralized Identity and IBM Verifiable Supply Chain deliver end-to-end credential management for enterprises and regulatory compliance in supply chain, finance, and beyond.
Startup And Open Source Options
Tools such as Dock Web3 Identity, Ceramic, and Wallet SDKs foster rapid development, open governance, and high adaptability, serving forward-thinking startups, researchers, and developers.
Domain-Based Identity Providers
ENS, Unstoppable Domains, and specialized platforms like #HashtagSpace turn blockchain-anchored domains into portable, verifiable digital identities. NFT Domains Explained and Endless Domains Ownership showcase their roles in login, attribution, and cross-platform identity.
Selection Criteria
Evaluating platforms means weighing factors such as:
- Security standards
- VC and DID method support
- Scalability
- UX and developer ecosystem
- Compliance and integration effort
Pilot projects and Decentralized Identity Platforms Comparison resources assist decision-makers.
Commercial Considerations
Platforms like #HashtagSpace and others seamlessly enable affiliate programs and marketing via on-chain attribution, creating new revenue models for creators. The web3 affiliate marketing platform approach disrupts legacy CPA/CPL networks by reducing fraud, boosting transparency, and respecting privacy, making it a compelling tool for digital commerce teams.
Identity Platforms Comparison
| Platform | Focus/Use | Pricing | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Decentralized ID | Enterprise, compliance | Enterprise | Big organizations |
| Dock | Credential/workflow dev | Hybrid | Startups, developers |
| IBM Verifiable Supply Chain | Supply chain, provenance | Consulting | Logistics/enterprises |
| ENS/NFT/#HashtagSpace | Portable domains/branding | One-time/market | Consumers/marketers |
Real-World Use Cases
The impact of web3 identity systems can be measured across major industries:
Healthcare Identity Use Cases
Secure patient-centric IDs, consent flows, auditable record access, and verifiable provider credentials (per Healthcare Secure Digital Identity). These reduce fraud, improve care coordination, and enable compliance in complex regulatory environments.
Financial Services
Reusable KYC credentials, privacy-protecting credit scoring, and frictionless onboarding are transforming finance. Blockchain-based domains ensure that user-facing platforms are both secure and easy to navigate (Testsite Blockchain Domains DeFi Identity).
Supply Chain And Provenance
IBM Verifiable Supply Chain details how credential-based workflows underpin supplier audits, compliance, and recall management, with every step auditable and resistant to tampering.
Consumer Identity And Commerce
Loginless ecommerce, NFT-based loyalty, and streamlined brand identity are all enabled by decentralized domain management (NFT Domains Explained). Marketers and creators enjoy new monetization methods and discoverability through domain and identity staking.
Measuring Impact
KPIs include fraud reduction rates, verification speed (cut from days to seconds), reduced onboarding friction, and measurable increases in user engagement, with pilots demonstrating 30–50% reductions in credential-related fraud across connected enterprises.
Developer Implementation Guide
Reference Architectures
Best practice for wallet-integrated credential flows is to maintain issuer, verifier, and user separation. Microservice patterns allow decoupled scaling and auditability. Sandboxed environments and testnets help teams test integration before real-world deployment.
SDKs And Libraries
Modern stacks include DID SDKs (JavaScript, Rust), wallet plugins, and issuer APIs. EveryCred Beginners Guide provides a developer-centric approach to onboarding, with detailed learning paths for VC formats, wallet management, and minimal verifier implementation.
Testing And Staging Strategies
Testnets, simulated revocations, and privacy stress testing are key for robust deployments. Support for VC revocation and interoperability testing strengthens reliability.
Migration Approaches
Incremental migration ensures coexistence with legacy flows (OAuth, SAML) while gradually introducing decentralized enhancements (as discussed in Microsoft Decentralized Identity).
Developer Resources And Next Steps
APIs, sample repos, standards guides, and a growing body of learning content (see Dock Web3 Identity) help teams move rapidly from prototype to production.
Governance Recovery And Control
Custody Models Reviewed
- Self-custody: Private key held solely by user, highest autonomy
- Managed custody: Hosted by provider, improves usability and recovery, but less user sovereignty
- Hybrid: Social or hardware key guardians, striking a balance
- Smart-Contract Wallets: Custom policy-based access, programmable for multi-sig or staged recovery
Recovery And Key Loss Solutions
Recovery can leverage social guardians, multi-sig, or custodial fallback — each blending varying degrees of security and usability. Smart contracts and hardware keys play an increasing role in robust, user-friendly recovery design.
Governance For DID Networks
Decentralized governance prevents any single party from unilaterally controlling DID registries. Proposals, upgrades, and parameter changes are driven via open or delegated stakeholder models.
Legal And UX Considerations
Regulatory obligations, such as GDPR or HIPAA, require careful UX and legal planning during implementation. Balancing frictionless user experience with strong recovery, privacy, and consent is key — as discussed in the Forbes Decentralized ID 2024 analysis.
Practical User Control Limits
Absolute control may be limited by real-world usability: users may forget keys or require legal intervention for recovery, and some regulated scenarios (KYC, AML) impose additional checks and oversight.
Future Trends And Outlook
The momentum behind web3 digital identity management is unstoppable. Standards convergence (W3C, blockchain consortia), maturation of privacy primitives like ZKPs, and cross-chain interoperability are transforming what is possible. The emergence of tokenized governance and decentralized reputation systems hint at a future where identity is both portable and programmable.
Enterprises and governments are piloting DIDs and VCs across healthcare, supply chains, and e-governance, with mainstream adoption forecast for the next 3–5 years. Continued investment in privacy, key management UX, and developer tooling will shape the pace and inclusivity of adoption.
The future of digital identity will be one where users, not institutions, assert control — enabled by cryptography, governed by open standards, and realized through global collaboration.
Common Questions Answered
What Is Web3 Digital Identity Management?
It is the practice of creating, controlling, and using digital identities via decentralized protocols rather than centralized providers. See Core Identity Fundamentals.
How Does Blockchain Improve Security?
Blockchain underpins unforgeable audit trails and tamper resistance while introducing advanced tools like ZKPs for privacy. Dive deeper in Security And Privacy Foundations.
Which Companies Offer Solutions?
Leading names include Microsoft Decentralized Identity, Dock Web3 Identity, IBM Verifiable Supply Chain, and a wave of domain and wallet providers like #HashtagSpace. See Platform Survey.
Can Users Fully Control Identity?
Control is greatly increased, but recovery and usability must be balanced. Explore custody, governance, and recovery in Governance Recovery And Control.
What Is The Future Of Identity Management?
Identity will become increasingly decentralized, privacy-centric, and cross-chain programmable. Learn more in Future Trends And Outlook.
Next Steps For Adoption
Actionable Next Steps
Developers: Set up a DID, issue or verify a sample VC using public SDKs and Web3 Domain Platform. Product teams: Pilot low-risk flows—loyalty, consent, or affiliate workflows—by integrating wallet or domain-based UX (Web3 Domain Services). Executives: Define policy, compliance, and vendor selection criteria, and champion participation in industry standard bodies. Each action accelerates the ecosystem’s shift toward secure, privacy-centric, and user-empowered identity for all.
For hands-on exploration, start experimenting with the tools available: NFT Domains Explained, Web3 Domain Services, and direct wallet integrations for issuing credentials. The time to participate is now — join the movement, experiment with a Web3 Domain Platform, and help build the open digital future.
Resources
- NFT Domains Explained
- Web3 Domain Services
- Web3 Domain Platform
- Dock Web3 Identity
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs Feature
- W3C DID Core
- Ethereum Decentralized Identity
- ArXiv Decentralized Identity Paper
- Healthcare Secure Digital Identity
- Decentralized Identity Platforms Comparison
- IBM Verifiable Supply Chain
- EveryCred Beginners Guide
- Microsoft Decentralized Identity
- Grandview Research Decentralized Identity Market
- Endless Domains Ownership
- Forbes Decentralized ID 2024
- Testsite Domains Identity Verification
- Testsite Decentralized Credentials Use Cases
- Testsite Blockchain Domains DeFi Identity
- Testsite Blockchain Domain Ownership
- Testsite Domain Lifecycle Management
- EndlessDomains Blog
- DevTo EveryCred Guide

Leave a Reply