Table of Contents
Introduction
In an era dominated by centralized giants, decentralized search engines are rising as groundbreaking alternatives that champion privacy, transparency, and user empowerment.
What is a Decentralized Search Engine?
Decentralized search engines represent a paradigm shift from traditional, centralized platforms like Google. Unlike those centralized entities that store vast amounts of user data on proprietary servers, decentralized search engines distribute indexing, data storage, and query processing across a network of independent nodes, often leveraging blockchain technology and peer-to-peer (P2P) systems. This structural difference mitigates risks of censorship and mass surveillance by removing single points of failure and control. Platforms such as Presearch and SwarmSearch embody this approach, allowing communities to collaboratively build and govern search indexes, while preserving user privacy.
Why Decentralize Search?
The motivation to decentralize search lies at the core of privacy protection, censorship resistance, and democratization of information. Centralized search engines have grown into powerful gatekeepers, often collecting detailed user profiles for targeted advertising and sometimes complying with content removal mandates. This model poses threats to user autonomy and free access to information.
By distributing control across numerous nodes, decentralized architectures enhance privacy by minimizing user tracking and eliminate central censorship possibilities. Moreover, decentralization fosters transparency through open-source algorithms and blockchain auditable records, empowering users to understand and influence the system’s operations. This shift aligns seamlessly with the principles of web3 domain management and user self-sovereignty, pivotal in today’s digital identity and autonomous internet paradigms.
How Decentralized Search Engines Work
Decentralized search engines rely on a sophisticated integration of distributed architecture, blockchain security, peer-to-peer networks, and token-based incentives to create a resilient, censorship-resistant search ecosystem.
Core Architecture
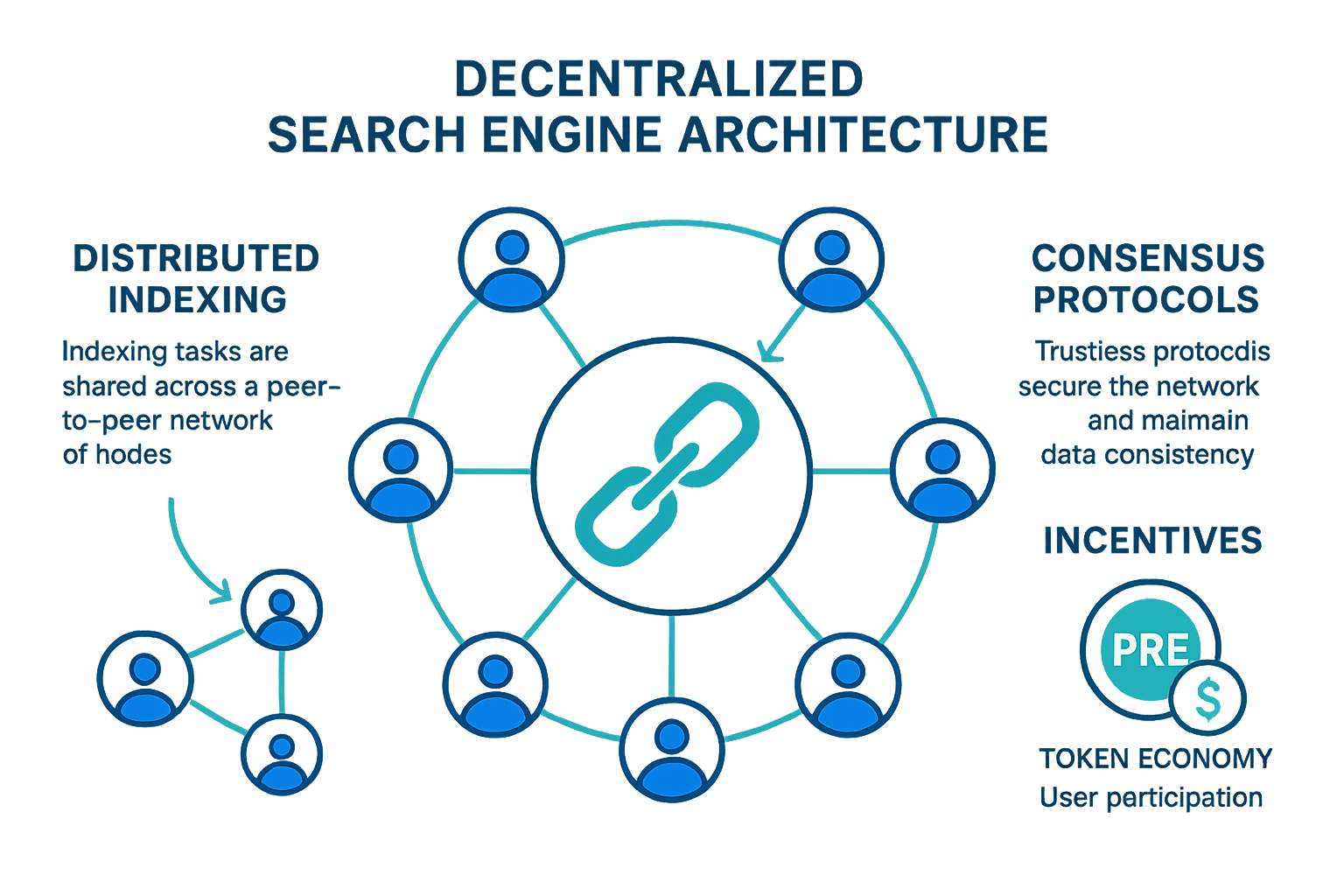
The backbone of decentralized search lies in distributed indexing and consensus protocols that collectively maintain an unbiased and secure search index.
Distributed Indexing
- Fault Tolerance: No single point of failure or attack.
- Scalability: Workload is balanced among many nodes.
- Censorship Resistance: Data removal or alteration require consensus, making suppression difficult.
Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus algorithms, such as Proof-of-Work (PoW), Proof-of-Stake (PoS), or Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS), ensure all nodes agree on the current state of the index and ranking. These protocols:
- Maintain data integrity and trust.
- Prevent malicious attacks or double-spending.
- Enable democratic network governance via community participation.
Key Insight: Consensus is critical to trustless operation, transforming disparate nodes into a unified search network.
Blockchain and P2P Networks
Blockchain Security
Blockchain immutability safeguards search data and user interactions, providing tamper-proof logs of all transactions such as indexing events, token rewards, and governance votes. Smart contracts automate transparent operations, preventing corruption.
Peer-to-Peer Architecture
P2P networks allow nodes to directly communicate, share data, and collaboratively handle queries without centralized servers. Benefits include:
- Enhanced resilience against censorship and attacks.
- Improved network scalability and latency.
- Distributed responsibility for indexing and querying.

Token Economy and Incentives
Tokens form the economic and governance core, motivating participation and fair operation.
User Rewards
Users and node operators receive tokens for contributing resources and activities like querying, validating data, or hosting nodes. For example, Presearch’s PRE tokens incentivize active search participation and network maintenance, fostering a vibrant ecosystem.
Governance Tokens
Governance tokens empower holders to vote on platform changes, development directions, and policy decisions, ensuring decentralized, community-driven control. This alignment balances incentives and sustains platform growth.
Benefits of Decentralized Search Engines
Privacy and Data Sovereignty
Unlike conventional engines that collect extensive personal data, decentralized alternatives operate without centralized tracking, employing:
- Encrypted queries and data anonymization.
- Pseudonymous or blockchain-based user identities.
- Zero-knowledge proofs and decentralized authentication.
This protects users from surveillance and data breaches, upholding data sovereignty and trust.
Censorship Resistance
By distributing content indexing and search logic, no single entity can dictate what information is accessible. This ensures:
- Unfiltered access to diverse viewpoints.
- Protection against political or commercial content suppression.
- Continuous availability despite external shutdown attempts.
Transparency and Trust
Open protocols and blockchain records provide visible governance and auditability. Communities can audit search algorithms, monitor node behavior, and participate in platform evolution, reinforcing user confidence.
Leading Decentralized Search Engines
Presearch Overview
Presearch is a community-driven platform rewarding users with PRE tokens for search activity and node operation. It features:
- Token-based incentives to foster engagement.
- An open, participatory governance model.
- Advertising integration that respects privacy.
SwarmSearch Overview
SwarmSearch harnesses AI on blockchain to deliver private, censorship-resistant search results. Its key elements include:
- AI-driven ranking and filtering.
- Self-funding economy enabling sustainability.
- Advanced token rewards and governance.
Other Notable Platforms
Emerging projects focus on niche improvements like decentralized identifiers, enhanced privacy layers, and interoperability with Web3 browsers. These platforms contribute to a diverse, rapidly maturing ecosystem.
Integration with Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Technical Integration Steps
Developers can embed decentralized search engines into dApps using:
- RESTful APIs and SDKs provided by platforms like Presearch.
- Smart contracts for governance and rewards automation.
- Peer-to-peer protocols ensuring data consistency.
Use Cases in Web3 Ecosystems
Common applications include:
- dApp discovery and indexing.
- Privacy-preserving resource search.
- Enhanced blockchain data retrieval.
Developer Resources and APIs
Accessible tools include SDKs, API documentation, open-source codebases, and community support forums. These empower rapid development and foster innovation within the Web3 landscape.
Decentralized Search vs. Google
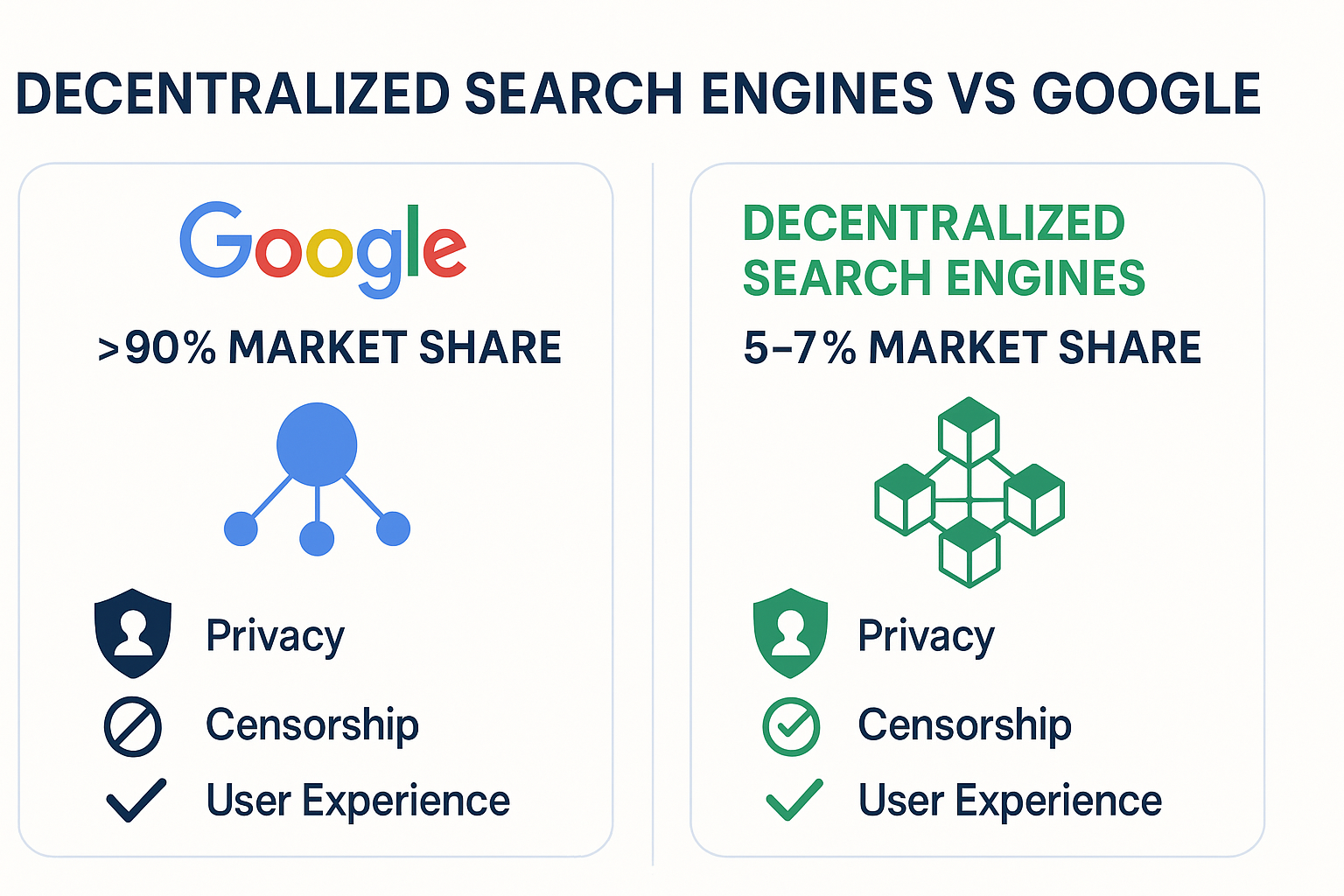
Privacy Comparison
Decentralized search engines prioritize privacy-first practices by avoiding mass data collection and employing cryptographic protections. Google, conversely, collects extensive user data for targeted advertising.
Censorship and Control
Centralized control allows Google to filter or suppress content due to legal or commercial pressures. Decentralized engines resist such control, maintaining open access to information.
User Experience and Performance
While Google currently excels in speed, interface polish, and search comprehensiveness, decentralized engines are rapidly improving, leveraging AI and optimized protocols. They offer trustworthy, user-empowering alternatives focused on transparency and privacy.
Challenges and Future Trends
Scalability and Performance
Scaling decentralized search remains complex due to distributed data management and consensus overheads. Innovations include sharding, layer 2 solutions, and AI-enhancements to optimize query processing and indexing.
Governance Models
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) and token-based governance frameworks continue evolving, enabling robust community control and network development aligned with user interests.
AI Integration and Innovation
AI’s growing role enhances search relevance, personalized results, and transparency via auditable, open algorithms. Combined with blockchain immutability, AI drives next-generation decentralized search capabilities.
Conclusion
The Future of Search
Decentralized search engines represent a pivotal evolution in online discovery, driven by imperatives of privacy, censorship resistance, and user autonomy. Ongoing innovations in blockchain, AI, and governance are converging to make these platforms increasingly viable and competitive alternatives to established giants.
Call to Action
Explore decentralized search engines today to enhance your online privacy, resist censorship, and join the future of transparent and user-controlled search. Join communities shaping the democratic, censorship-resistant web and secure your digital identity with web3 domain management.
References
- What is a Decentralized Search Engine and How Does it Work?
- Presearch – the Community-powered, Decentralized Search Engine
- SwarmSearch: Decentralized Search Engine with Self-Funding Economy
- Decentralized Search Engine Industry Analysis
- Decentralized Search Engine Implementation Guide
- Decentralized Intelligence Network White Paper
- Experts Call for Decentralized Search Engines
- Peer-Reviewed Research on Decentralized Search Engines
- Decentralized Search Engine Token Economy
- Decentralized Search Engine Governance Models
- Open Source Decentralized Search Projects
Leave a Reply